Application of Equilibrium Constant
Application of Equilibrium Constant: Overview
This topic covers concepts such as Degree of Dissociation for Equilibrium Reactions, Calculating Reaction Quotient, Applications of Equilibrium Constants, Predicting Direction of Reaction, Predicting Extent of Reaction, Reaction Quotient(Q), etc.
Important Questions on Application of Equilibrium Constant
When two reactants, A and B are mixed to give products C and D, the reaction quotient , at the initial stage of the reaction :–
Phosphorus pentachloride dissociates as follows, in a closed reaction vessel,
If total pressure at equilibrium of the reaction mixture is P and degree of dissociation of is , the partial pressure of will be :
Consider three vessels containing aqueous solutions of a weak acid (initial concentration , degree of dissociation ), another weak acid (initial concentration , degree of dissociation ), and their mixture (initial concentration of , degree of dissociation and initial concentration of , degree of dissociation ), respectively. When and are varied, the correct plot (assuming and to be small) is
The above reaction is studied graphically as shown in the figure.
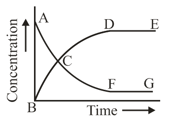
Which of the following statements are correct?
gas dissociates according to the equation, . When heated to the density of the gas mixture at and at equilibrium is . The degree of dissociation of at is
When the reaction was studied, it was observed that the initial concentration of was times that of and the equilibrium concentrations of and were equal. Then for the given equilibrium equals
Identify the correct expression for the equilibrium constant of the following reaction:
mole of mole of and mole of are taken in a flask to obtain the following equilibrium:
If the equilibrium constant for the reaction is . Predict the direction of the reaction.
For the above reaction, vessel contains and moles of and respectively. Then, what will happen to the reaction?
The reaction quotient predicts:
In an aqueous solution of volume when the reaction of reached equilibrium the was . When of water is further added, at the new equilibrium will be :-
The equilibrium constant for the reaction between and to form and , at is . For the following composition of the reaction mixture, decide which of the following option is correct?
A mixture of and has a vapour density of at . What is the number of moles of in of the mixture?
| Column I | Column II |
| (A) Equilibrium const. | (p) Reaction will shift forward |
| (B) Volume of vessel Equilibrium constant |
(q) Reaction will shift backward |
| (C) |
(r) Reaction is in equilibrium |
| (D) Helium gas is added to the reaction mixture at equilibrium keeping the pressure constant. |
(s) Reaction may shift in the forward or backward direction. |
The equilibrium constant for the reaction between and to form and , at is . For the following composition of the reaction mixture, decide which of the following option is correct?
The equilibrium constant for the reaction, is
Calculate the equilibrium concentration of , if mole of and mole of are placed in flask and allowed to attain the equilibrium.
The equilibrium constant(K) for the reaction Cyclohexane Hex-1-ene is 10732. At the given condition in a closed one litre vessel 2 moles of cyclohexane are mixed with 2 moles of hex-1-ene then
Initial pressure of is 800 mm and total pressure at equilibrium is 900 mm of Hg. Calculate the percentage of dissociated in the following reaction:
